Methanol, a simple alcohol with the chemical formula CH₃OH, plays a significant role in the petrochemical industry. Its applications and significance in the industry include:

Feedstock for Chemical Production:
Formaldehyde: One of the primary uses of methanol is in the production of formaldehyde, which is used to manufacture resins, plastics, and adhesives.
Acetic Acid: Methanol is also a key feedstock in the production of acetic acid, an essential chemical for producing vinyl acetate monomer (VAM), which is used in paints, adhesives, and coatings.
Methyl Tertiary-Butyl Ether (MTBE): Methanol is used to produce MTBE, an additive for gasoline that helps increase octane levels and reduce engine knocking.
Solvent and Antifreeze:
Methanol serves as a solvent in the chemical industry for various reactions and processes.
It is used as an antifreeze in pipelines and windshield washer fluid due to its low freezing point.
Fuel Applications:
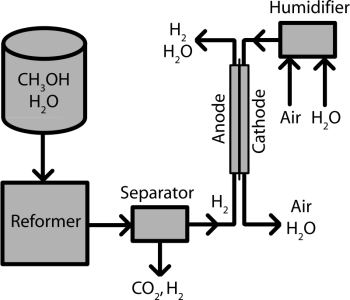
Direct Fuel: Methanol can be used directly as a fuel in internal combustion engines or blended with gasoline.
Biodiesel Production: Methanol is a crucial component in the transesterification process for producing biodiesel from vegetable oils or animal fats.
Methanol-to-Gasoline (MTG): This process converts methanol into gasoline, providing an alternative route for producing transportation fuels.
Renewable Energy Source:
Methanol can be produced from biomass, natural gas, or even carbon dioxide, making it a versatile option for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
It is used in fuel cells as a source of hydrogen for generating electricity in a clean and efficient manner.
Intermediate in the Production of Other Chemicals:
Methanol is used to synthesize a variety of chemicals, including methylamines, methyl methacrylate (used in acrylic plastics), and dimethyl ether (DME, used as an aerosol propellant and a potential diesel substitute).
The versatility and wide range of applications make methanol a cornerstone of the petrochemical industry. Its production and utilization are critical for various industrial processes, contributing to the production of essential materials and alternative fuels